Describe the General Characteristics of Cartilage
Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that provides structural support protects the organs underlying it forms attachments and frameworks. Chondrocytes are first chondroblast cells that produce the collagen extracellular matrix ECM and then get.
Its cells regenerate faster when damaged or worn away.

. Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook. The non-cellular component of connective tissue is called the extracellular matrix. Chapter 6 1 What are the locations and general characteristics of cartilage.
A notochord a dorsal hollow tubular nerve cord pharyngeal gill arches or slits a post-anal tail and an endostylethyroid gland Figure 2. Textbook solution for Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 14th Edition David N. Flexible - loose adipose fibrous.
Cartilage forms the structural model for the developing bones. It can withstand force but it can also bend. Cartilage is a semi-rigid but flexible avascular connective tissue found at various sites within the body.
Provides framework and attachments protects underlying tissues forms structural models of developing bones and lacks a direct blood supply. Cartilage Extracellular Matrix ECM Cartilage ECM is composed of. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that differs from bone in several ways.
Describe the locations. Describe the general characteristics of cartilage. Answer to Describe the general characteristics of cartilage.
Cartilage- tough connective tissue. Describe the cells and extracellular matrix of bone. Examples of specialized connective tissue include blood bone cartilage and lymphoid tissue.
The characteristics of cartilage is chondrocytes and collagen which allows nutrients to diffuse between blood vessels. Describe the two methods of cartilage formation. Cartilage is the only component of the skeletons of certain primitive vertebrates including lampreys and sharks.
For one the primary cell types are chondrocytes as opposed to osteocytes. This lack of blood and lymph supply makes the growth and healing of cartilage slow and challenging. Describe the general characteristics of cartilage.
These substances make the ECM firm and resistant to mechanical forces. The most important functions of cartilage include. 2 Be able to match the description of cartilaginous growth with its correct name.
It also helps to cushion joints. General Characteristics of Connective Tissues. Compare the function and composition of the three types of cartilage.
In general cartilage has the following functions and characteristics. Compare and contrast immature and mature bone. Dense Connective Tissue- have more fibers and fewer fibers than loose CT.
Abundance of intercellular material between them matrix Rigid - bone cartilage. Find step-by-step Anatomy and physiology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question. Animals in the phylum Chordata share five key chacteristics that appear at some stage during their development.
4 Know the structural composition of a long bone as it was. Cartilage and Bone Lecture Objectives Describe the general functions of cartilage and bone. It cushions surfaces so they dont touch directly.
It is primary form of cartilage that makes up articular joint surfaces. Three general characteristics of connective tissue are that they are highly vascularized they recover well from damage and they possess a lot of non-cellular material. Solutions for Chapter 5 Problem 13P.
Cartilage is a firm yet flexible fibrous tissue found at various sites in the body. Start your trial now. Its made of cells chondroblasts and chondrocytes and extracellular matrix.
Describe the general characteristics of cartilage. All cartilage is unique in that it doesnt have a blood supply nerve connections or connections to the lymphatic system like other structures in the body. First week only 499.
Loose Connective Tissue- loosely woven. Dense regular CT ordered parallel CT gives. Areolar found in the skin blood vessels mucous membranes.
While more rigid and less flexible than muscle cartilage is not as stiff as bone. Helps repair tissue damage. It is composed of a dense network of collagen fibres embedded in a firm gelatinous ground substance that has the consistency of plastic.
Chapter 5 Problem 18P. Matching 3 What are the classifications of bone according to shape and be able to provide examples of those types of bones in the body. Farther apart than epithelial cells.
Cartilage is rigid composed of collagen fibers and chondrocytes embedded in a gel-like ground substance provides support. Describe the two methods of bone formation. Cartilage is a specialized supporting connective tissue composed of cells and extracellular matrix.
Solution for What are some general characteristics of chondrin that make it adaptive to the function of cartilage. Cartilage is a robust and viscoelastic connective tissue that can be found in joints between bones the rib cage intervertebral discs the ear and the nose. We have step-by-step solutions for.
Collagen andor elastic fibers Lots of GAGs and proteoglycans Nice choices. With a pliable structure composed primarily of water this tissue type is also extremely tough. Cartilage is a tough elastic connective tissue.
In some groups some of these key chacteristics are present only during embryonic development. This structure gives the tissue tensile strength enabling it to bear weight while retaining greater flexibility than bone. Its rigid but flexible.
Cartilage is strong and sort of rigid but also flexible. Cartilage gives shape support and structure to other body tissues.

What Is Cartilage Definition Types Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Epithelial Tissue Types Google Search Tissue Biology Tissue Types Human Anatomy And Physiology

Cartilage And Bone Kristine Krafts M D Cartilage And Bone Lecture Objectives Describe The General Functions Of Cartilage And Bone Compare The Function Ppt Download

Characteristics Of Synovial Joints This Joint Is In 3 Types Unilateral Rotation Only About One Axes Biaxial Moveme Synovial Joint Joint Bone And Joint
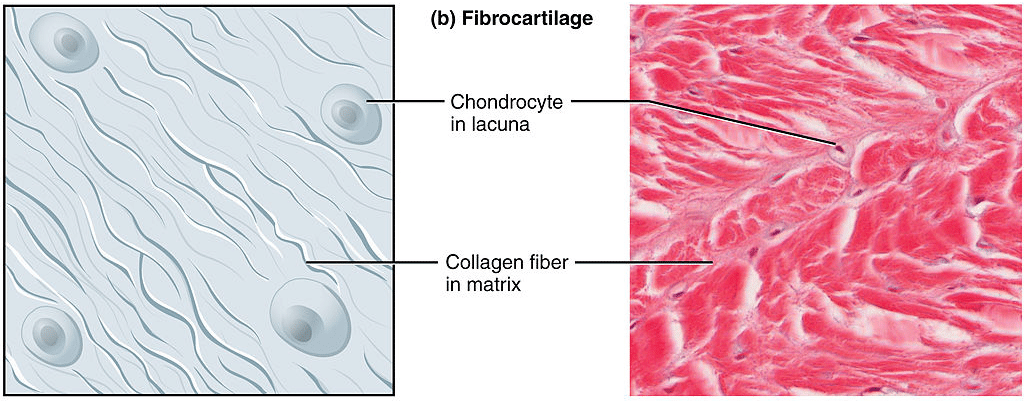
Cartilage Hyaline Elastic Fibrocartilage Teachmephysiology

Here We See Another Dipiction Of Simple Vs Stratified Epithelia Simple Eplihelia As Well As Pseudo St Tissue Biology Cells And Tissues Anatomy And Physiology

Pin By Sarah Riley On Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Elastic
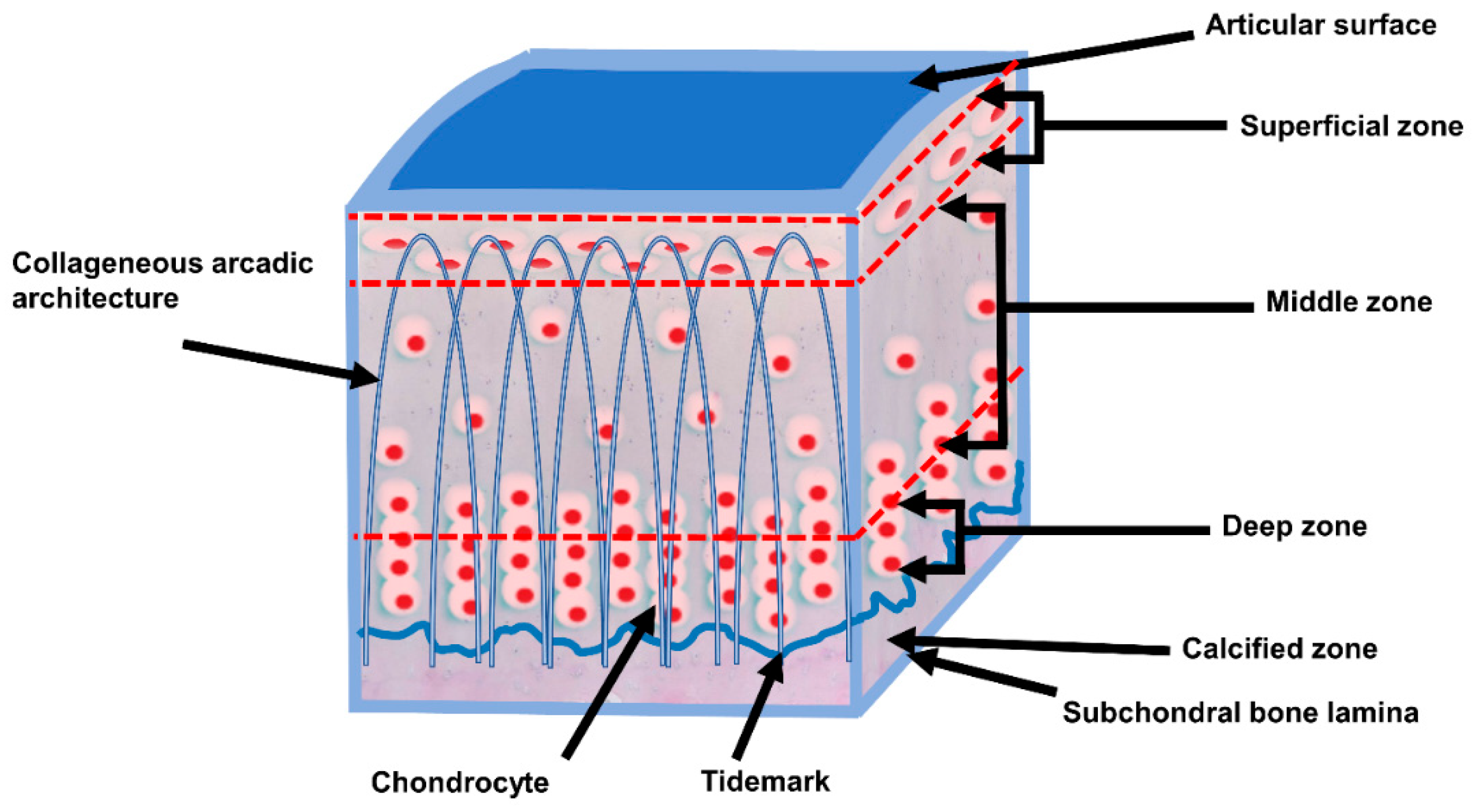
Life Free Full Text The Biomechanics Of Cartilage An Overview Html

Cartilage Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
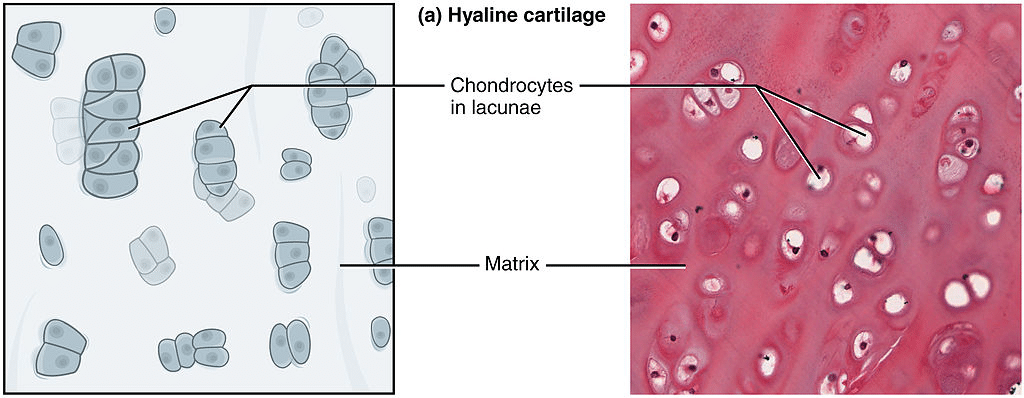
Cartilage Hyaline Elastic Fibrocartilage Teachmephysiology

Cartilage Definition Function And Types Biology Dictionary
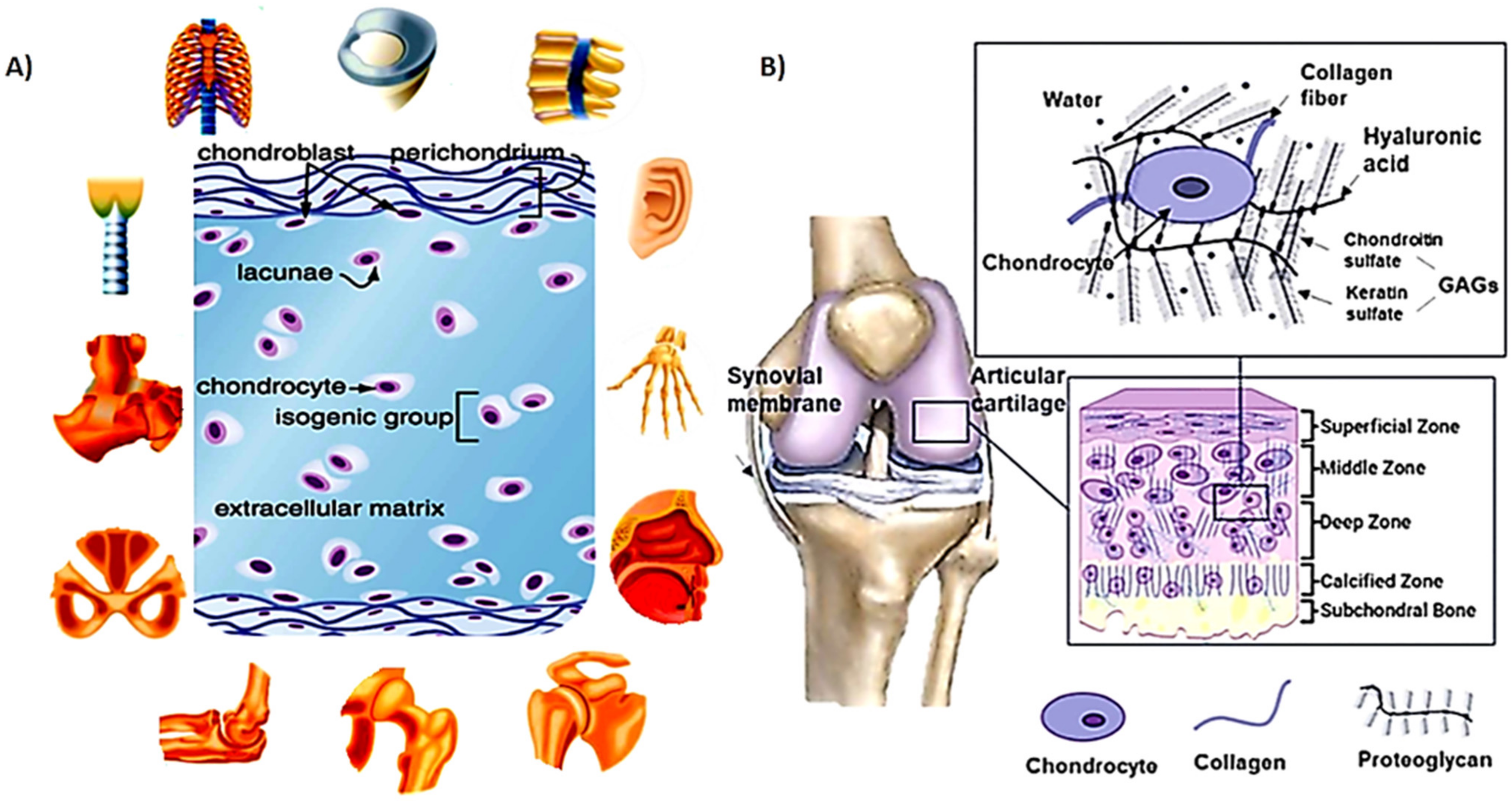
Polymers Free Full Text Advanced Hydrogels For Cartilage Tissue Engineering Recent Progress And Future Directions Html
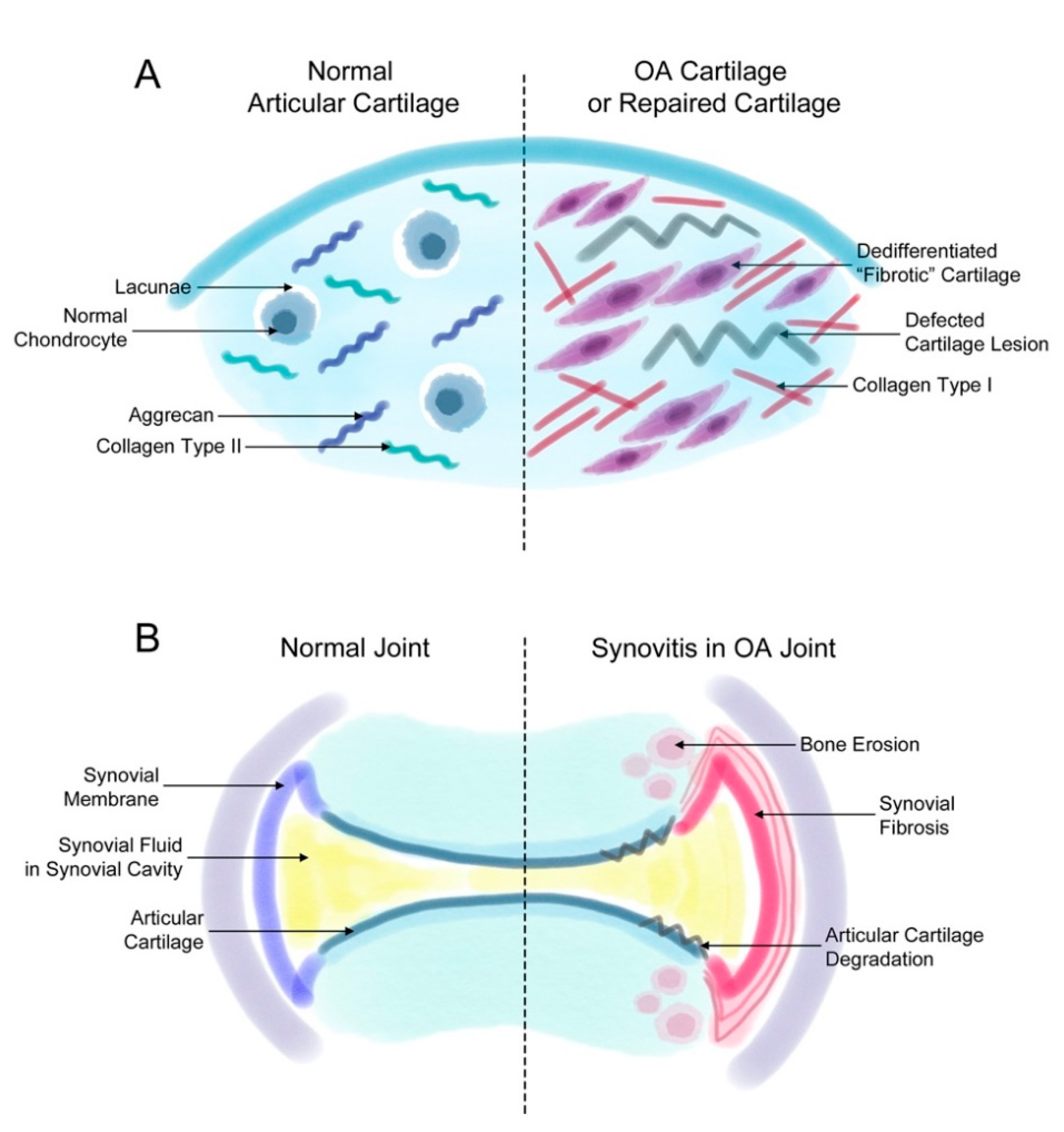
Life Free Full Text The Role Of Fibrosis In Osteoarthritis Progression Html

Cartilage And Bones Hyaline Cartilage Cartilage Tissue Types

Tissue Biology Medical Laboratory Science Physiology

What Is Cartilage Definition Types Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


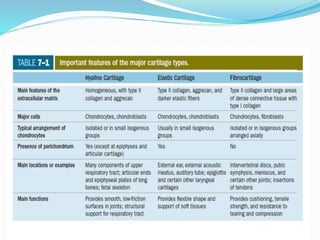
Comments
Post a Comment